August 30, 2023
Modbus gateways and concentrators in substation application

Update 2024/02/26:
The Transforming Powergrid Communication article series is now available as a full brochure in PDF format. Click here to download.
Modbus is a widely used communication protocol in industrial automation and control systems. Its simplicity and versatility have contributed to its continued use in various applications, notably in power substations where voltage is transformed, controlled, and distributed.
Common variants of the Modbus protocol include Modbus RTU, Modbus ASCII, and Modbus TCP. The first two are serial-based, facilitating communications with operational devices such as relays, meters, controllers, and protection equipment. Modbus RTU is a compact binary protocol known for its efficiency and compactness, well-suited for applications with lower data rates. Modbus ASCII uses human-readable ASCII characters for data transmission. It is less efficient than Modbus RTU due to the overhead of ASCII character encoding, but can be useful for debugging and testing purposes.
Modbus TCP, on the other hand, works with Ethernet, enabling higher data rates as well as more advanced control and monitoring features. It is the key to bridging legacy devices with modern Ethernet systems, such as those based on the IEC61850 standard.
By converting Modbus RTU and ASCII to Modbus TCP, Modbus serial devices can continue to play active roles in substation operation, while newer Ethernet-based SCADA and cybersecurity measures are brought in to ensure the high availability, reliability, and security that modern power grids need. No need to upgrade the whole communications network—a good Modbus gateway (such as ATOP MB5201) is all it takes to integrate legacy devices with a smart, advanced system.

Meanwhile, Modbus gateways can serve more than simple protocol conversion. Port isolation and VPN features (such as provided by ATOP MB5901 and MB5904D) protect against potential failures and attacks by ensuring that issues on one side of the gateway do not propagate across to critical devices. Routing and filtering functions help control the flow of information, managing data traffic and optimizing communication between devices. Data mapping assigns data points into memory, further improving communication efficiency.
A Modbus concentrator, in particular (such as the ATOP MB5916-CT and MB5916A-CT), is an advanced machine suitable for frequent polling requests from multiple devices. It performs pre-defined Modbus commands to read/write data automatically from slave devices. It then mirrors the obtained slave device data to its own memory, compartmenting those from different slaves in separate tables for easy access. Thus, requesting masters can receive responses in a shorter period, achieving better overall efficiency, even with a high density of devices.
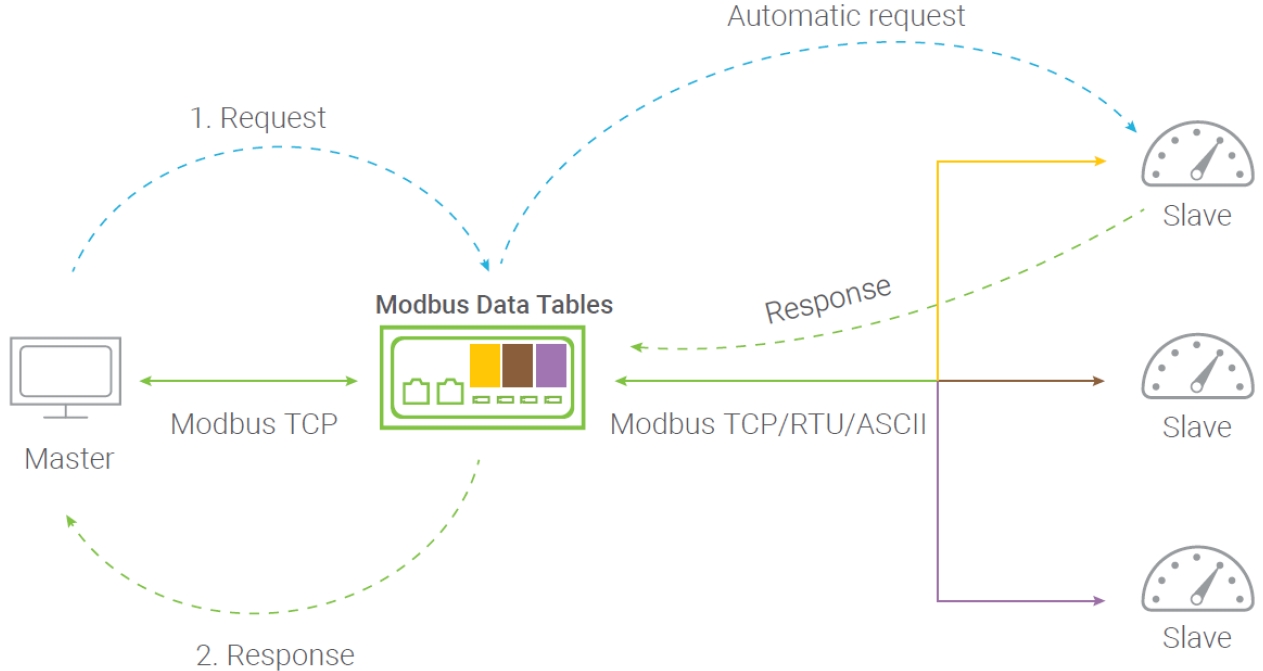
Modbus concentrator register mapping can be customized for optimal performance where different masters need to access different data structures. Link status and data timestamp access allow high-level management, and for the most mission critical applications, redundant architecture can achieve automatic link recovery in case of Ethernet or serial link failure.
Do you have a Modbus application in need of upgrade? Talk to our experts about getting the most out of ATOP Modbus gateways and Modbus concentrators.